Color coding the periodic table student worksheet is an engaging and effective tool for students to learn about the elements and their properties. By assigning different colors to different groups of elements, students can easily identify patterns and relationships within the periodic table, making it easier to understand and remember the vast amount of information it contains.
This worksheet provides a comprehensive overview of the periodic table, including its organization, the different color-coding methods, and how to use color coding to identify element properties and predict their behavior. With its clear explanations, engaging activities, and real-world examples, this worksheet is an invaluable resource for students of all levels.
1. Introduction
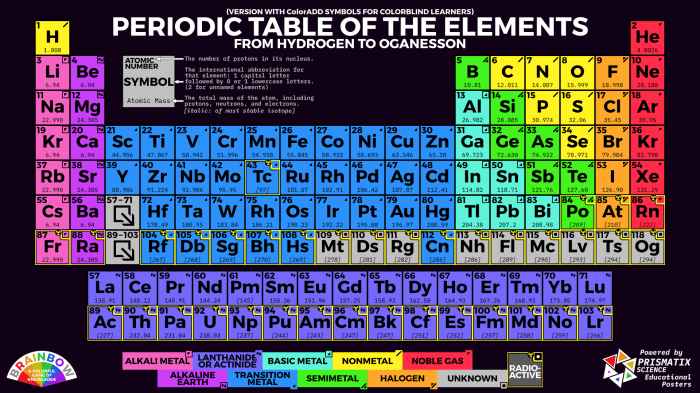
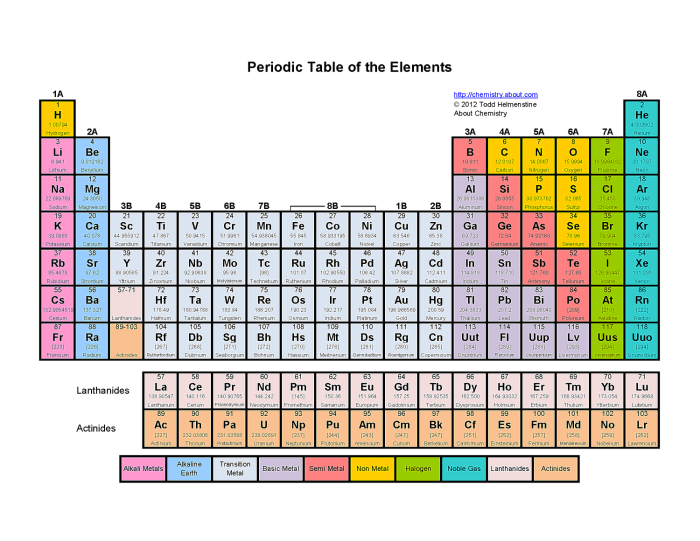
The periodic table is a tabular arrangement of chemical elements, organized based on their atomic number, electron configurations, and recurring chemical properties. Color coding the periodic table is a visual technique that assigns specific colors to different groups of elements, making it easier for students to identify and understand their properties and relationships.
Color coding helps students quickly recognize patterns and trends within the periodic table. It allows them to visualize the similarities and differences between elements and groups, facilitating their understanding of chemical bonding, reactivity, and other important concepts.
2. Elements and Their Properties
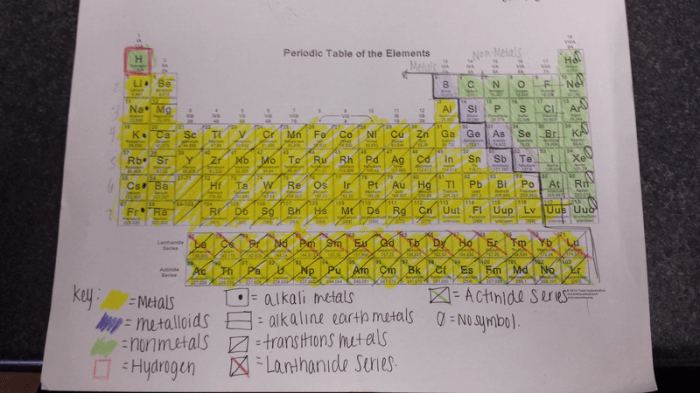
The periodic table can be divided into several groups based on the color coding system. The following table provides a brief overview of the main groups and their associated colors:
| Group | Color | Elements |
|---|---|---|
| Alkali Metals | Red | Lithium, Sodium, Potassium, Rubidium, Cesium, Francium |
| Alkaline Earth Metals | Green | Beryllium, Magnesium, Calcium, Strontium, Barium, Radium |
| Transition Metals | Blue | Scandium, Titanium, Vanadium, Chromium, Manganese, Iron, Cobalt, Nickel, Copper, Zinc, Gallium, Germanium, Arsenic, Selenium, Bromine, Krypton |
| Metalloids | Purple | Boron, Silicon, Germanium, Arsenic, Antimony, Tellurium, Polonium |
Each element in the periodic table has a unique symbol, atomic number, and atomic mass. The atomic number represents the number of protons in the nucleus, while the atomic mass is the weighted average mass of the isotopes of that element.
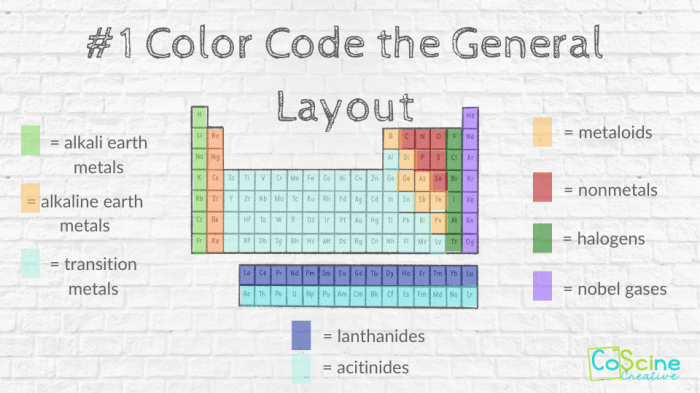
3. Color Coding Methods
There are several different methods for color coding the periodic table. The most common methods include:
- By Atomic Number:Assigns colors to elements based on their atomic number, with the colors repeating every 18 elements.
- By Group:Assigns colors to elements based on their group in the periodic table, with each group having a different color.
- By Reactivity:Assigns colors to elements based on their reactivity, with more reactive elements being assigned brighter colors.
Each method has its own advantages and disadvantages. The atomic number method is simple and easy to understand, but it does not provide much information about the chemical properties of the elements. The group method provides more information about the chemical properties of the elements, but it can be more difficult to understand.
The reactivity method is useful for understanding the reactivity of the elements, but it does not provide much information about their other properties.
4. Student Worksheet
A student worksheet that incorporates color coding can help students understand the periodic table. The worksheet can include activities such as:
- Matching elements to their colors
- Identifying patterns in the periodic table
- Predicting the properties of an element based on its color
These activities can help students learn about the periodic table and its organization, as well as the properties of the elements.
5. Applications and Examples
Color coding the periodic table has a wide range of applications in different fields, including:
- Chemistry:Color coding can help students and researchers visualize the relationships between elements and their properties, facilitating the understanding of chemical reactions and bonding.
- Education:Color coding can make the periodic table more accessible and engaging for students, aiding in their comprehension of chemistry concepts.
- Research:Color coding can assist researchers in identifying patterns and trends in the periodic table, leading to new discoveries and insights.
While color coding provides numerous benefits, it also has limitations. The choice of colors may vary depending on the specific application, and the colors assigned to certain groups may not always reflect their actual chemical properties.
FAQ Resource: Color Coding The Periodic Table Student Worksheet
What are the benefits of using color coding to learn the periodic table?
Color coding the periodic table helps students identify patterns and relationships between elements, making it easier to understand and remember their properties and behavior.
What are the different methods for color coding the periodic table?
The periodic table can be color-coded by atomic number, group, reactivity, or other properties. Each method has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the best method for a particular student will depend on their learning style and goals.
How can I use color coding to predict the properties of an element?
By identifying the color group of an element, students can make predictions about its properties based on the properties of other elements in the same group. For example, all alkali metals (Group 1) are highly reactive and form 1+ ions.