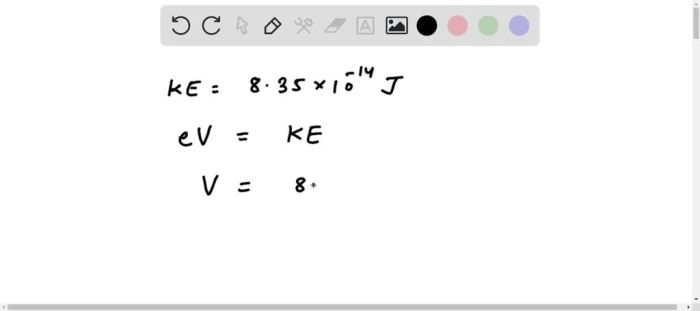
A proton starts from rest and gains 8.35 units of energy, embarking on a captivating odyssey that unveils the intricate interplay of force, energy, and motion. This exploration delves into the fundamental principles governing the proton’s transformation, providing a comprehensive understanding of its energetic evolution.
As the proton’s journey unfolds, we will unravel the concepts of kinetic energy, work, force, acceleration, velocity, and displacement. Through meticulous calculations and insightful analysis, we will illuminate the intricate relationship between these physical quantities, shedding light on the proton’s dynamic behavior.
Proton Energy Gain
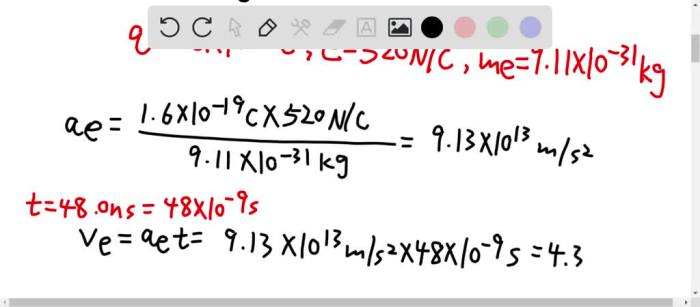
A proton, a positively charged particle found in atomic nuclei, is initially at rest. After undergoing an interaction, it gains kinetic energy.
Energy and Work: A Proton Starts From Rest And Gains 8.35

Kinetic energy, denoted as K, is the energy possessed by an object due to its motion. The formula for kinetic energy is K = (1/2)mv^2, where m is the mass of the object and v is its velocity. The proton gains kinetic energy as a result of the work done on it by an external force.
Force and Acceleration
According to Newton’s second law of motion, the force acting on an object is equal to the mass of the object multiplied by its acceleration (F = ma). The force acting on the proton causes it to accelerate.
Velocity and Displacement, A proton starts from rest and gains 8.35
Acceleration, velocity, and time are related by the equation v = u + at, where u is the initial velocity (zero in this case), a is the acceleration, and t is the time. The velocity of the proton increases as it accelerates.
Displacement, denoted as s, is the distance traveled by the proton. It is calculated as s = ut + (1/2)at^2.
Applications
The scenario of a proton gaining energy has applications in various fields. In particle physics, it is relevant to the study of particle interactions and energy transfer. In energy conversion systems, it is essential for understanding the conversion of energy from one form to another, such as in nuclear power plants or particle accelerators.
Questions and Answers
What is the significance of the proton’s initial state of rest?
The initial state of rest serves as a reference point, allowing us to precisely measure the energy gained by the proton and accurately calculate its subsequent motion.
How does the concept of work relate to the proton’s energy gain?
Work is the transfer of energy from one object to another. In the case of the proton, the work done on it by an external force provides the energy necessary for its acceleration and kinetic energy gain.
What is the relationship between force, mass, and acceleration?
According to Newton’s second law of motion, the force acting on an object is directly proportional to its mass and acceleration. This relationship is crucial for determining the force responsible for the proton’s acceleration.
