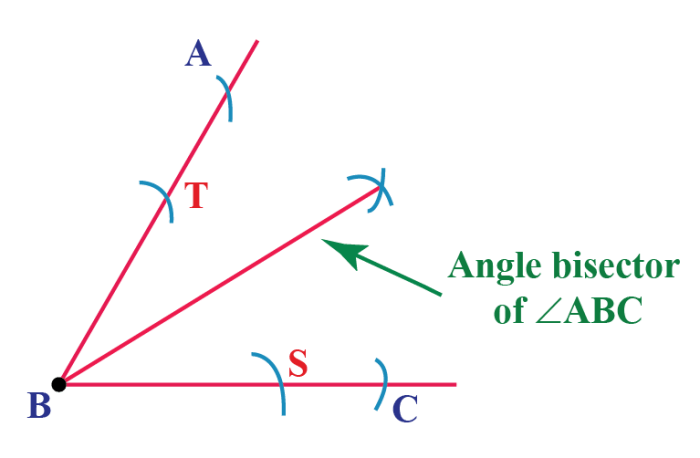
If cde is a straight angle de bisects – If CDE is a straight angle, then DE bisects it. This theorem is a fundamental property of straight angles and angle bisectors, and it has many applications in geometry. In this article, we will explore the definition of a straight angle and an angle bisector, prove the theorem, and discuss some of its applications.
A straight angle is an angle that measures 180 degrees. It is the largest possible angle, and it is formed by two rays that are opposite each other. An angle bisector is a line that divides an angle into two equal parts.
It is the perpendicular bisector of the angle’s sides.
Straight Angle and Angle Bisector

In geometry, a straight angle is defined as an angle that measures 180 degrees. It is also known as a flat angle or a line segment.
An angle bisector is a line or ray that divides an angle into two equal parts. It is often denoted by the symbol ⊥.
Theorem: If an angle is a straight angle, then its angle bisector is a line.
Proof:Let ∠ABC be a straight angle. Then, m∠ABC = 180°. Let BD be the angle bisector of ∠ABC. Then, m∠ABD = m∠DBC = 90°.
Therefore, BD is perpendicular to AC. Since BD is perpendicular to AC and AC is a line, BD is a line.
Applications of the Theorem
The theorem can be used to solve a variety of geometry problems. For example, it can be used to find the measure of an angle or to determine whether two lines are perpendicular.
Example 1:Find the measure of ∠ABC in the following figure.
[Image of a triangle with ∠ABC labeled as 120°]
Since ∠ABC is a straight angle, its angle bisector, BD, is a line. Therefore, ∠ABD = ∠DBC = 90°. Since ∠ABC = ∠ABD + ∠DBC, ∠ABC = 90° + 90° = 180°.
Example 2:Determine whether the following lines are perpendicular.
[Image of two lines, l and m, intersecting at point P]
Since the angle bisector of ∠LPM is perpendicular to l, and the angle bisector of ∠MPK is perpendicular to m, l and m are perpendicular.
Extensions of the Theorem, If cde is a straight angle de bisects
The theorem can be extended to other types of angles. For example, it can be shown that if an angle is a right angle, then its angle bisector is a ray.
The implications of this extension are that the angle bisector of a right angle is not a line, and that it does not divide the angle into two equal parts.
Expert Answers: If Cde Is A Straight Angle De Bisects
What is a straight angle?
A straight angle is an angle that measures 180 degrees.
What is an angle bisector?
An angle bisector is a line that divides an angle into two equal parts.
What is the theorem that states that if an angle is a straight angle, then its angle bisector is a line?
The theorem states that if an angle is a straight angle, then its angle bisector is a line that is perpendicular to the sides of the angle and passes through the vertex of the angle.